Goal: Automate the inspection of the bearing conformance test to applicable internal/industry specifications.
Why was this important?
- Quality management desired to reduce the time spent performing the test as well as reduce conflicts between inspectors and manufacturing management.
- Reduce human bias during the conformance test.
What was the process before changes were implemented?
- Swage operator documents machine setup details on form, prepares the first article or last swaged piece and submits the form with the first article (or last swaged piece) into the inspection queue.
- Assigned inspector conducts the conformance test (peel test and gap measurements).
- Based on the type of bearing, lines are scribed for the documentation specified measurement locations (ex: AS9100D, AS81820).
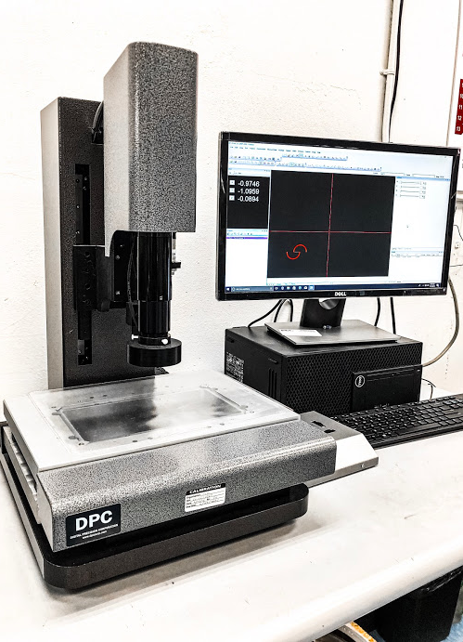
- Measurements of the race to ball gap are measured at the scribed locations with the use of an optical measurement device.
- If failed, an MRR (Material Rejection Review) document is initiated and the form with the test piece is moved for review by a Quality Engineer, where further lot tests can take place.
- If passed, the lot may proceed through its manufacturing process.
How was the goal realized?
- I revised all specifications that were required to be adhered to.
- I compiled the pertinent criteria.
- The internal specification had conflicts when I reviewed it against industry/customer specifications. Corrections/changes were submitted to the design department.
- If the internal specification did not cover a subset of products. Changes with references to industry/customer specifications were submitted to the design department.
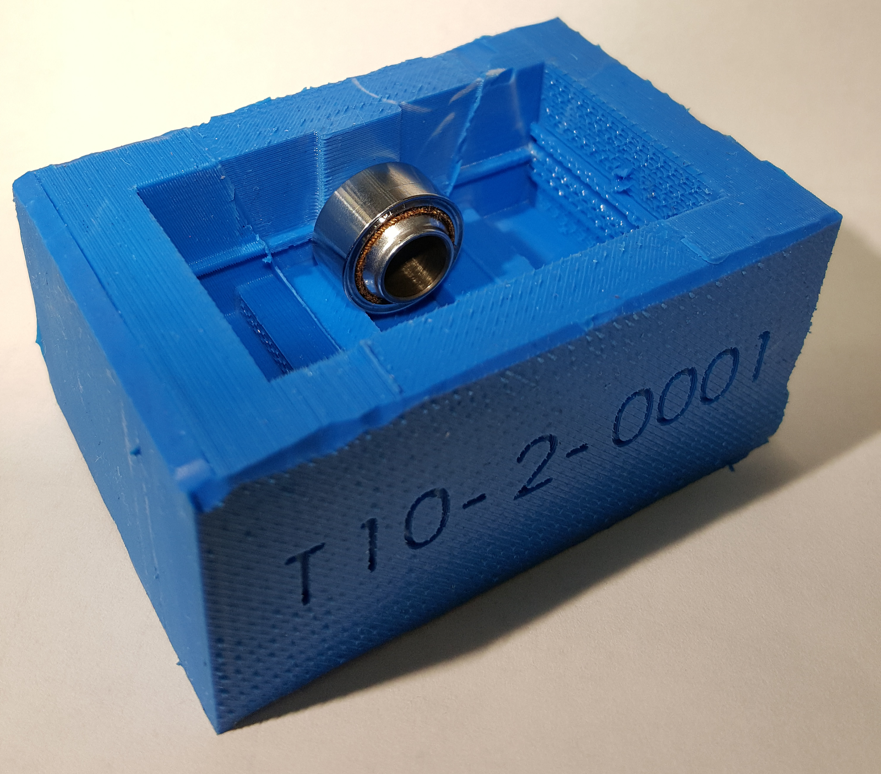
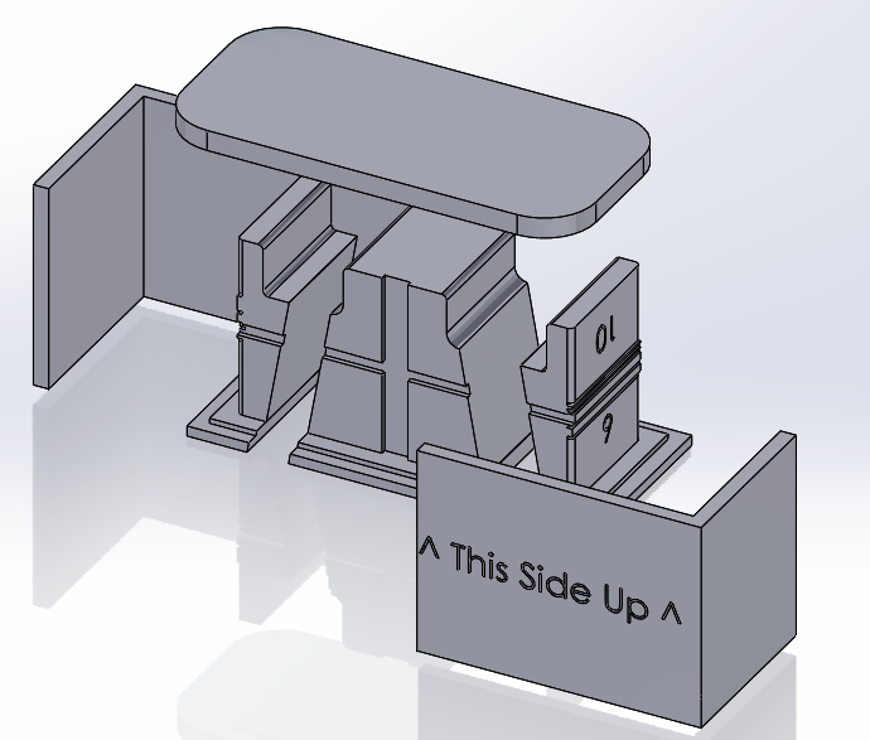
- Tooling and bearing conformance test prep. process adjustments were developed to allow for the VMM (Vision Measurement Machine) to locate the bearing in its mold as well as ensuring a consistent sanded surface.
- RTV molds were developed to ensure consistent positioning in the acrylic mold.
- For larger bearings, this tool greatly aided the operator in reducing the effort required to remove the test specimen from the previous metal molds.
- Alternate epoxies were investigated for consistincies in their cure volume.
- Sanding procedures were adjusted to ensure true visibility of the race-to-ball gap of the bearing.
- Tooling was developed to ensure the sanded bearing surface was parallel to the VMM's surface plate.
- A locating bracket was placed to ensure the VMM can locate the bearing looking in the same general location. All tooling was adjusted to ensure consistency was possible despite human error.
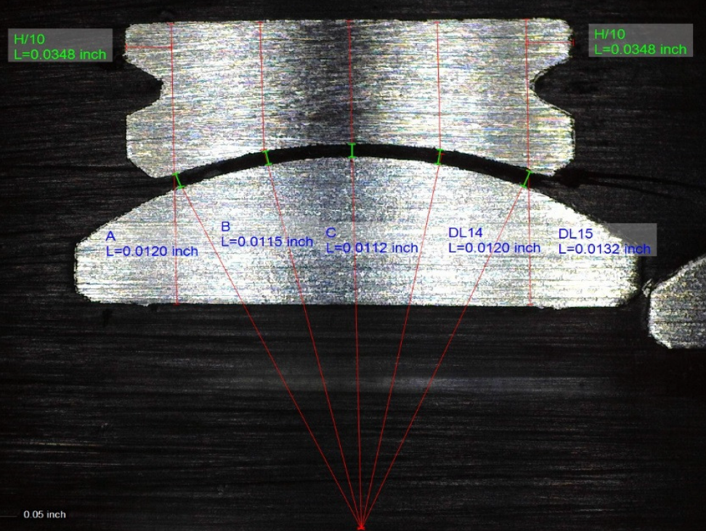
Results
Initial implementation required much training for the inspectors to become accustomed to the VMM, in addition to the new inspection process.
The automation proved itself reliable in test results, and once inspectors were able to get comfortable with the new process, false positive rejections were drastically reduced.